Oops
Java OOPs Concepts
- Object-Oriented Programming
- Advantage of OOPs over Process-oriented programming language
- Difference between Object-oriented and Object-based programming language.
In this page, we will larn about the nuts of OOPs. Object-Oriented Programming is a paradigm that provides many concepts, such as inheritance, data binding, polymorphism, etc.
Simula is considered the first object-oriented programming language. The programming epitome where everything is represented as an object is known as a truly object-oriented programming language.
Smalltalk is considered the commencement truly object-oriented programming linguistic communication.
The pop object-oriented languages are Coffee, C#, PHP, Python, C++, etc.
The chief aim of object-oriented programming is to implement real-world entities, for case, object, classes, abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism, etc.
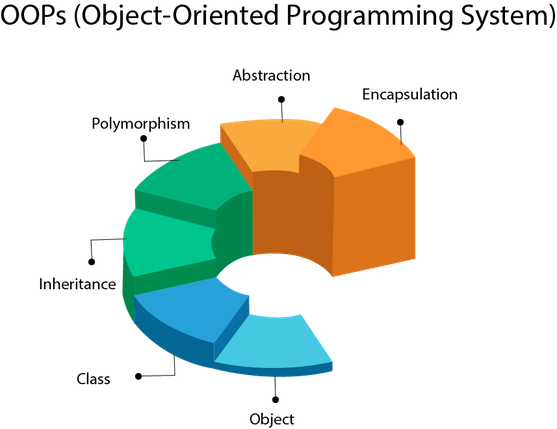
OOPs (Object-Oriented Programming Arrangement)
Object means a existent-globe entity such as a pen, chair, tabular array, computer, sentinel, etc. Object-Oriented Programming is a methodology or prototype to pattern a program using classes and objects. It simplifies software evolution and maintenance by providing some concepts:
- Object
- Class
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
Autonomously from these concepts, there are some other terms which are used in Object-Oriented blueprint:
- Coupling
- Cohesion
- Association
- Aggregation
- Composition
Object

Any entity that has state and behavior is known as an object. For example, a chair, pen, tabular array, keyboard, cycle, etc. It tin can be physical or logical.
An Object can exist defined as an instance of a course. An object contains an address and takes upward some space in memory. Objects can communicate without knowing the details of each other'due south data or code. The merely necessary thing is the type of bulletin accepted and the type of response returned by the objects.
Case: A canis familiaris is an object because it has states similar color, name, breed, etc. as well as behaviors like wagging the tail, barking, eating, etc.
Course
Collection of objects is called class. It is a logical entity.
A form can also be defined as a design from which yous can create an individual object. Class doesn't consume whatsoever space.
Inheritance
When i object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object, it is known as inheritance. Information technology provides lawmaking reusability. It is used to accomplish runtime polymorphism.

Polymorphism
If ane task is performed in different ways, it is known every bit polymorphism. For example: to convince the customer differently, to draw something, for example, shape, triangle, rectangle, etc.
In Coffee, we use method overloading and method overriding to achieve polymorphism.
Some other instance tin be to speak something; for example, a cat speaks meow, canis familiaris barks woof, etc.
Abstraction
Hiding internal details and showing functionality is known as abstraction. For example phone telephone call, we don't know the internal processing.
In Java, we utilise abstruse grade and interface to achieve brainchild.

Encapsulation
Binding (or wrapping) lawmaking and data together into a single unit are known as encapsulation. For instance, a sheathing, information technology is wrapped with different medicines.
A java class is the example of encapsulation. Java bean is the fully encapsulated course because all the data members are individual here.
Coupling
Coupling refers to the noesis or information or dependency of another class. It arises when classes are aware of each other. If a course has the details information of some other class, there is strong coupling. In Java, we use private, protected, and public modifiers to display the visibility level of a class, method, and field. You can employ interfaces for the weaker coupling because at that place is no concrete implementation.
Cohesion
Cohesion refers to the level of a component which performs a single well-defined task. A single well-defined task is done by a highly cohesive method. The weakly cohesive method volition dissever the task into separate parts. The coffee.io package is a highly cohesive package considering it has I/O related classes and interface. Nonetheless, the java.util bundle is a weakly cohesive package because it has unrelated classes and interfaces.
Clan
Association represents the human relationship between the objects. Hither, i object tin can be associated with one object or many objects. There can be four types of clan between the objects:
- 1 to One
- I to Many
- Many to I, and
- Many to Many
Let's understand the human relationship with existent-fourth dimension examples. For case, One state tin can take one prime number minister (i to ane), and a prime number minister tin have many ministers (one to many). Also, many MP's can accept ane prime number government minister (many to one), and many ministers tin can have many departments (many to many).
Association tin exist undirectional or bidirectional.
Aggregation
Aggregation is a way to achieve Association. Assemblage represents the relationship where 1 object contains other objects as a part of its state. Information technology represents the weak relationship between objects. Information technology is as well termed as a has-a relationship in Java. Like, inheritance represents the is-a relationship. Information technology is another manner to reuse objects.
Composition
The composition is likewise a style to reach Association. The composition represents the relationship where one object contains other objects equally a part of its state. There is a stiff human relationship between the containing object and the dependent object. It is the country where containing objects practise not have an contained existence. If you lot delete the parent object, all the child objects volition exist deleted automatically.
Advantage of OOPs over Procedure-oriented programming language
1) OOPs makes development and maintenance easier, whereas, in a procedure-oriented programming linguistic communication, it is non piece of cake to manage if code grows as project size increases.
ii) OOPs provides data hiding, whereas, in a procedure-oriented programming language, global data tin can be accessed from anywhere.

Figure: Information Representation in Procedure-Oriented Programming
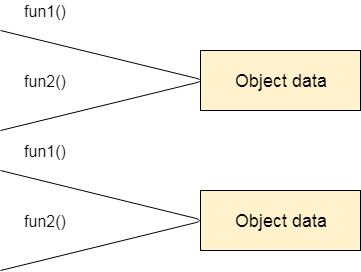
Figure: Information Representation in Object-Oriented Programming
3) OOPs provides the power to simulate real-world event much more effectively. We tin can provide the solution of existent word problem if we are using the Object-Oriented Programming linguistic communication.
What is the difference betwixt an object-oriented programming language and object-based programming language?
Object-based programming linguistic communication follows all the features of OOPs except Inheritance. JavaScript and VBScript are examples of object-based programming languages.
livingstonbusteding.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/java-oops-concepts
0 Response to "Oops"
Post a Comment